垃圾回收
参考文档
如何判断对象可以回收
引用计数法
参考文章
基本介绍
- 引用计数法(reference counting)。它的做法是为每个对象添加一个引用计数器,用来统计指向该对象的引用个数。一旦某个对象的引用计数器 为 0,则说明该对象已经死亡,便可以被回收了。
- 具体实现如下 :
- 如果有一个引用,被赋值为某一对象,那么将该对象的引用计数器 +1。
- 如果一个指向某一对象的引用,被赋值为其他值,那么将该对象的引用计数器 -1。也就是说,我们需要截获所有的引用更新操作,并且相应地增减目标对象的引用计数器
优势与缺陷
优点 :
- 简单,直接,不需要暂停整个应用。
缺点 :
- 需要编译器的配合,编译器要生成特殊的指令来进行引用计数的操作;
- 不能处理循环引用的问题。比如对象 A 中有一个字段指向了对象 B ,而对象 B 中也有一个字段指向了对象 A,而事实上他们俩都不再使用,但计数器的值永远都不可能为 0 ,也就不会被回收,然后就发生了内存泄露。
- 但是引用计数法其实是很难解决对象之间相互循环引用的问题,所以,Java虚拟机里面没有选用引用计数算法来管理内存。
代码案例
使用 -XX:+PrintGCDetails 打印GC信息
package cn.knightzz.reference.count; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: ReferenceCountingGC * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 引用计数法测试 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-09 10:54 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class ReferenceCountingGC { public Object instance = null; private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024; /** * 这个成员属性的唯一意思就是占点内存,以便能在GC日志中看清楚是否被回收过 */ private byte[] bigSize = new byte[2 * _1MB]; public static void testGC() { ReferenceCountingGC objA = new ReferenceCountingGC(); ReferenceCountingGC objB = new ReferenceCountingGC(); objA.instance = objB; objB.instance = objA; //假设在这行发生gc,objA和ObjB是否能被回收 System.gc(); } public static void main(String[] args) { testGC(); } }
执行结果如下 :
[GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 9338K->5096K(152576K)] 9338K->5104K(500736K), 0.0024104 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 5096K->0K(152576K)] [ParOldGen: 8K->4853K(348160K)] 5104K->4853K(500736K), [Metaspace: 3147K->3147K(1056768K)], 0.0039136 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] Heap PSYoungGen total 152576K, used 6554K [0x0000000716000000, 0x0000000720a00000, 0x00000007c0000000) eden space 131072K, 5% used [0x0000000716000000,0x0000000716666850,0x000000071e000000) from space 21504K, 0% used [0x000000071e000000,0x000000071e000000,0x000000071f500000) to space 21504K, 0% used [0x000000071f500000,0x000000071f500000,0x0000000720a00000) ParOldGen total 348160K, used 4853K [0x00000005c2000000, 0x00000005d7400000, 0x0000000716000000) object space 348160K, 1% used [0x00000005c2000000,0x00000005c24bd718,0x00000005d7400000) Metaspace used 3156K, capacity 4496K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 343K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到,其实也是有被回收了,也就是意味着虚拟机并没有因为两个对象相互引用就不回收他们。侧面说明虚拟机并不是通过引用计数法来判断对象是否存活。
虽然可引用计数法很简单,也经常被提及,但是HotSpot虚拟机却不是用这个算法来判断对象是否继续被引用,而是使用下面要介绍的算法:可达性分析算法。
可达性分析算法
参考论文
基本介绍
目前 Java 虚拟机的主流垃圾回收器采取的是可达性分析算法。这个算法的实质在于将一系列 GC Roots 作为初始的存活对象合集(live set),然后从该合集出发,探索所有能够被 该集合引用到的对象,并将其加入到该集合中,这个过程我们也称之为标记(mark)。最终,未被探索到的对象便是死亡的,是可以回收的。
算法的基本思路就是通过一系列称为GC Roots的对象作为起始点,从这些节点开始向下搜索,搜索走过的路径被称为引用链,当一个对象到GC Roots没有任何引用链相连时,则证明此对象不可用的。
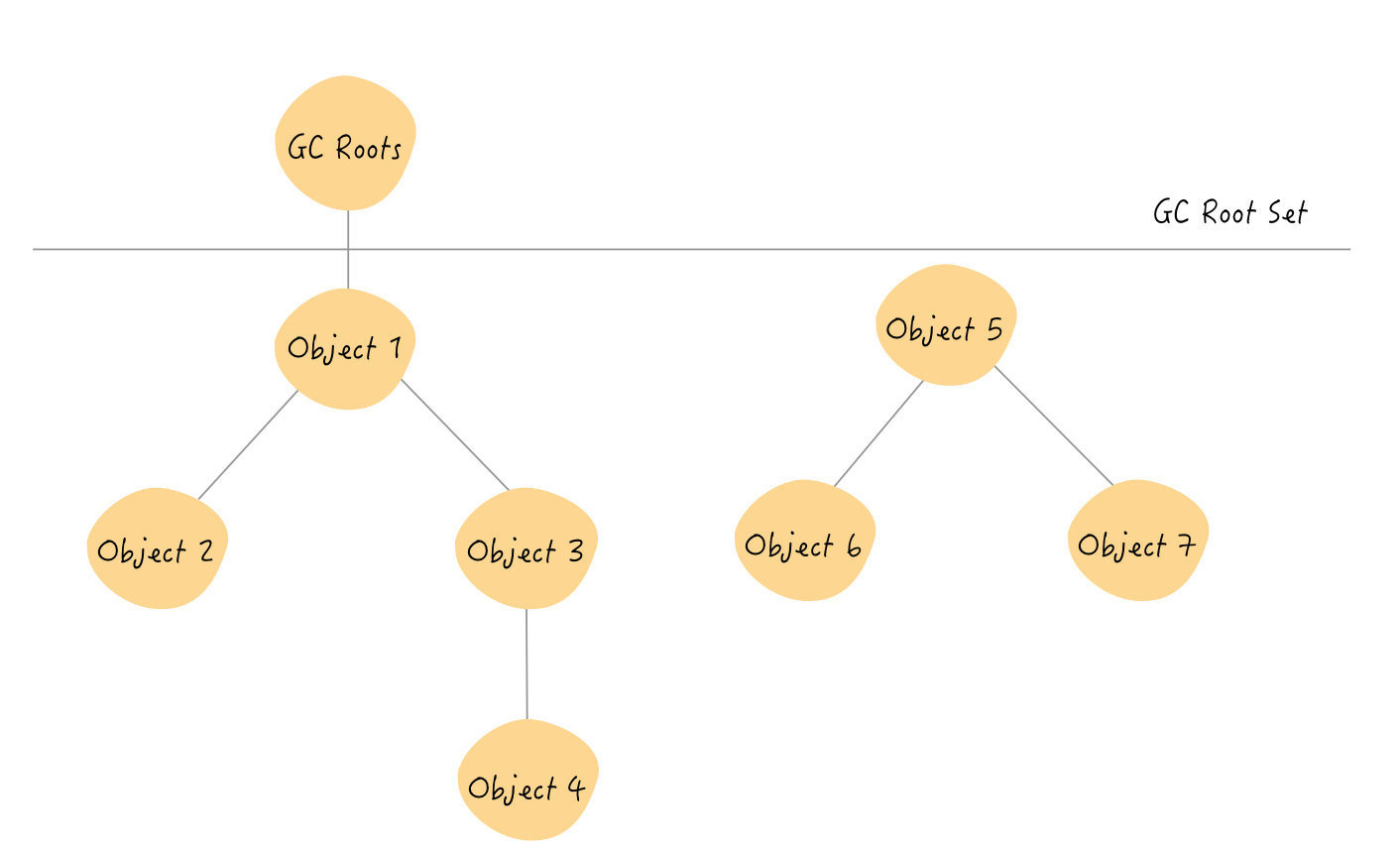
Object1 ~ Object4 都可以被GC Root访问到,而Object5~Object7都不可以被访问到,这也就是说。也就是说,Object5、6、7这三个对象就是不可达的,下次垃圾回收的时候,可能就会被回收掉。
根是什么?
根就可以理解为main方法,你main方法就是根,你这这里new出来的对象,就是最开始的根,比如A。
根可达就是从main方法往里面找,一直能找到最末尾的都是可达的,比如CD,但是 EFH三个,从根是找不到的,这就是垃圾。
可以作为GC Roots的对象 :
- Java 方法栈桢中的局部变量
- 已加载类的静态变量
- 已启动且未停止的 Java 线程
- 本地方法栈中JNI(即一般说的Native方法)引用的对象
-
首先第一种是虚拟机栈中的引用的对象,我们在程序中正常创建一个对象,对象会在堆上开辟一块空间,同时会将这块空间的地址作为引用保存到虚拟机栈中,如果对象生命周期结束了,那么引用就会从虚拟机栈中出栈,因此如果在虚拟机栈中有引用,就说明这个对象还是有用的,这种情况是最常见的。
-
第二种是我们在类中定义了全局的静态的对象,也就是使用了
static关键字,由于虚拟机栈是线程私有的,所以这种对象的引用会保存在共有的方法区中,显然将方法区中的静态引用作为GC Roots是必须的。 -
第三种便是常量引用,就是使用了
static final关键字,由于这种引用初始化之后不会修改,所以方法区常量池里的引用的对象也应该作为GC Roots。 -
最后一种是在使用JNI技术时,有时候单纯的Java代码并不能满足我们的需求,我们可能需要在Java中调用C或C++的代码,因此会使用native方法,JVM内存中专门有一块本地方法栈,用来保存这些对象的引用,所以本地方法栈中引用的对象也会被作为
GC Roots。
可达性分析可以解决引用计数法所不能解决的循环引用问题。举例来说,即便对象 a 和 b 相互引用,只要从 GC Roots 出发无法到达 a 或者 b,那么可达性分析便不会将它们加入存活对象合集之中。
两次引用
为了增加垃圾收集的灵活性。实际上,一个到 GC Roots 没有任何引用链相连的对象有可能在某一个条件下 复活 自己。对象的状态可以简单分成三类:
- 可达的: 从根节点开始, 可以到达这个对象。(实际上可触及对象也分为四种:)
- 可复活的: 对象的所有引用都被释放, 但是对象有可能在finalize()函数中复活。
- 不可触及的:对象对象没有覆盖finalize()方法或者finalize()函数已经被调用,并且没有复活,那么就会进入不可触及状态,不可触及的对象不可能被复活,因为finalize()函数只会被调用一次。
四种引用方式
参考文章 :
既然是引用计数法,那肯定就有各种引用 :
- 强引用
- 软引用
- 弱引用
- 虚引用
JDK1.2之后,Java对引用的概念进行了扩充,将引用分为强引用(Strong Reference)、软引用(Soft Reference)、弱引用(Weak Reference)、虚引用(Phantom Reference)4种。
JDK1.2之前,只有被引用和没有被引用两种状态
强引用
- 一般指的是对像被new出来,强引用一般不会被JVM收回,但会报OutOfMemory(内存不足)
- 指在程序代码之中普遍存在的,类似
Object obj = new Object()这类的引用,只要强引用还存在,垃圾收集器永远不会回收被引用的对象 - 只有所有 GC Roots 对象都不通过强引用引用该对象,该对象才能被垃圾回收
强引用如何断开 : Dog dog = new Dog() 强引用, => dog 引用了 Dog 对象, 当 dog = null 引用断开
软引用
- 用来描述一些还有用但并非必需的对象。对于软引用关联着的对象,在系统将要发生内存溢出异常之前,将会把这些对象列进回收范围之中进行第二次回收。如果这次回收还没有足够的内存,才会抛出内存溢出异常。在
JDK1.2之后,提供了SoftReference类来实现软引用 - 仅有软引用引用该对象时,在垃圾回收后,内存仍不足时会再次出发垃圾回收,回收软引用对象
- 可以配合引用队列来释放软引用自身
- 软引用就是把对象用SoftReference包裹一下,当我们需要从软引用对象获得包裹的对象,只要get一下就可以了:
- 当内存不足,会触发JVM的GC,如果GC后,内存还是不足,就会把软引用的包裹的对象给干掉,也就是只有在内存不足,JVM才会回收该对象。
使用 SoftReference 实现软引用 :
public static void soft() { // list --> SoftReference --> byte[] List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { SoftReference<byte[]> ref = new SoftReference<>(new byte[_4MB]); System.out.println(ref.get()); list.add(ref); System.out.println(list.size()); } System.out.println("循环结束:" + list.size()); for (SoftReference<byte[]> ref : list) { System.out.println(ref.get()); } }
软引用回收小案例 :
SoftReference<byte[]> softReference = new SoftReference<byte[]>(new byte[1024*1024*10]); System.out.println(softReference.get()); System.gc(); System.out.println(softReference.get()); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10]; System.out.println(softReference.get());
运行程序,需要带上一个参数:-Xmx20M
[B@11d7fff [B@11d7fff null
可以很清楚的看到手动完成GC后,软引用对象包裹的byte[]还活的好好的,但是当我们创建了一个10M的byte[]后,最大堆内存不够了,所以把软引用对象包裹的byte[]给干掉了,如果不干掉,就会抛出OOM。
软引用到底有什么用呢?比较适合用作缓存,当内存足够,可以正常的拿到缓存,当内存不够,就会先干掉缓存,不至于马上抛出OOM。
软引用可以和一个引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用。如果软引用所引用对象被垃圾回收,JAVA虚拟机就会把这个软引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
ReferenceQueue<String> referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>(); String str = new String("abc"); SoftReference<String> softReference = new SoftReference<>(str, referenceQueue); str = null; // Notify GC System.gc(); System.out.println(softReference.get()); // abc Reference<? extends String> reference = referenceQueue.poll(); System.out.println(reference); //null
注意:软引用对象是在jvm内存不够的时候才会被回收,我们调用System.gc()方法只是起通知作用,JVM什么时候扫描回收对象是JVM自己的状态决定的。就算扫描到软引用对象也不一定会回收它,只有内存不够的时候才会回收。
当内存不足时,JVM首先将软引用中的对象引用置为null,然后通知垃圾回收器进行回收:
if(JVM内存不足) { // 将软引用中的对象引用置为null str = null; // 通知垃圾回收器进行回收 System.gc(); }
也就是说,垃圾收集线程会在虚拟机抛出OutOfMemoryError之前回收软引用对象,而且虚拟机会尽可能优先回收长时间闲置不用的软引用对象。对那些刚构建的或刚使用过的**"较新的"软对象会被虚拟机尽可能保留**,这就是引入引用队列ReferenceQueue的原因。
应用场景 :
浏览器的后退按钮。按后退时,这个后退时显示的网页内容是重新进行请求还是从缓存中取出呢?这就要看具体的实现策略了。
- 如果一个网页在浏览结束时就进行内容的回收,则按后退查看前面浏览过的页面时,需要重新构建;
- 如果将浏览过的网页存储到内存中会造成内存的大量浪费,甚至会造成内存溢出。
这时候就可以使用软引用,很好的解决了实际的问题:
// 获取浏览器对象进行浏览 Browser browser = new Browser(); // 从后台程序加载浏览页面 BrowserPage page = browser.getPage(); // 将浏览完毕的页面置为软引用 SoftReference softReference = new SoftReference(page); // 回退或者再次浏览此页面时 if(softReference.get() != null) { // 内存充足,还没有被回收器回收,直接获取缓存 page = softReference.get(); } else { // 内存不足,软引用的对象已经回收 page = browser.getPage(); // 重新构建软引用 softReference = new SoftReference(page); }
弱引用
弱引用(WeakReference):
- 仅有弱引用引用该对象时,在垃圾回收时,无论内存是否充足,**都会回收弱引用对象 **,[
可以看下面的小案例来理解] - 可以配合引用队列来释放弱引用自身
弱引用与软引用的区别在于:只具有弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。在垃圾回收器线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域的过程中,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。不过,由于垃圾回收器是一个优先级很低的线程,因此不一定会很快发现那些只具有弱引用的对象。
String str = new String("abc"); WeakReference<String> weakReference = new WeakReference<>(str); str = null;
JVM首先将软引用中的对象引用置为null,然后通知垃圾回收器进行回收:
str = null; System.gc();
注意:如果一个对象是偶尔(很少)的使用,并且希望在使用时随时就能获取到,但又不想影响此对象的垃圾收集,那么你应该用Weak Reference来记住此对象。
下面的代码会让一个弱引用再次变为一个强引用:
String str = new String("abc"); WeakReference<String> weakReference = new WeakReference<>(str); // 弱引用转强引用 String strongReference = weakReference.get();
同样,弱引用可以和一个引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用,如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
弱引用是只要垃圾回收器扫描到就会直接被回收掉 :
package cn.knightzz.reference.weak; import java.lang.ref.WeakReference; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: WeakReferenceTest * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 弱引用测试 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-10 17:05 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class WeakReferenceTest { private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc weakReference(); } public static void weakReference() throws InterruptedException { // list --> WeakReference --> byte[] List<WeakReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { WeakReference<byte[]> ref = new WeakReference<>(new byte[_4MB]); list.add(ref); } System.out.print("循环结束:" + list.size() + " "); for (WeakReference<byte[]> reference : list) { System.out.print(reference.get() + " "); } System.out.println(); // 通知垃圾收集器 System.gc(); System.out.println("已经通知 GC"); System.out.println("等待3s后垃圾回收完"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); System.out.print("垃圾回收完毕, 打印虚引用 "); for (WeakReference<byte[]> reference : list) { System.out.print(reference.get() + " "); } } }
如上面的代码所示 :
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 2176K->504K(6144K)] 14464K->13117K(19968K), 0.0007463 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] 循环结束:4 [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d [B@355da254 [GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 4712K->496K(6144K)] 17325K->13213K(19968K), 0.0004718 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 496K->0K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12717K->768K(13824K)] 13213K->768K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3236K->3236K(1056768K)], 0.0046600 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] 已经通知 GC 等待3s后垃圾回收完 垃圾回收完毕, 打印虚引用 null null null null Heap PSYoungGen total 6144K, used 1267K [0x00000000ff980000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) eden space 5632K, 22% used [0x00000000ff980000,0x00000000ffabce28,0x00000000fff00000) from space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff80000,0x00000000fff80000,0x0000000100000000) to space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff80000) ParOldGen total 13824K, used 768K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff980000, 0x00000000ff980000) object space 13824K, 5% used [0x00000000fec00000,0x00000000fecc0188,0x00000000ff980000) Metaspace used 3770K, capacity 4540K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 415K, capacity 428K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到循环结束以后, 四个对象都是存在的, 没被回收, 但是: 当我们通知垃圾回收器回收后, 所有的byte[]对象都会被回收掉,
虚引用
虚引用(PhantomReference):
- 必须配合引用队列使用,主要配合 ByteBuffffer 使用,被引用对象回收时,会将虚引用入队,由 Reference Handler 线程调用虚引用相关方法释放直接内存
虚引用是最弱的一种引用关系,如果一个对象仅持有虚引用,那么它就和没有任何引用一样,它随时可能会被回收,在 JDK1.2 之后,用 PhantomReference 类来表示
通过查看这个类的源码,发现它只有一个构造函数和一个 get() 方法,而且它的 get() 方法仅仅是返回一个null,
也就是说将永远无法通过虚引用来获取对象,虚引用必须要和 ReferenceQueue 引用队列一起使用 , 因为PhantomReference 仅有一个构造方法
public class PhantomReference<T> extends Reference<T> { /** * Returns this reference object's referent. Because the referent of a * phantom reference is always inaccessible, this method always returns * <code>null</code>. * * @return <code>null</code> */ public T get() { return null; } public PhantomReference(T referent, ReferenceQueue<? super T> q) { super(referent, q); } }
应用场景:
虚引用主要用来跟踪对象被垃圾回收器回收的活动。 虚引用与软引用和弱引用的一个区别在于:
- 虚引用必须和引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用。当垃圾回收器准备回收一个对象时,如果发现它还有虚引用,就会在回收对象的内存之前,把这个虚引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
String str = new String("abc"); ReferenceQueue queue = new ReferenceQueue(); // 创建虚引用,要求必须与一个引用队列关联 PhantomReference pr = new PhantomReference(str, queue);
程序可以通过判断引用队列中是否已经加入了虚引用,来了解被引用的对象是否将要进行垃圾回收。如果程序发现某个虚引用已经被加入到引用队列,那么就可以在所引用的对象的内存被回收之前采取必要的行动。
终结器引用
终结器引用(FinalReference):
-
无需手动编码,但其内部配合引用队列使用,在垃圾回收时,终结器引用入队(被引用对象暂时没有被回收),再由 Finalizer 线程通过终结器引用找到被引用对象并调用它的 fifinalize
方法,第二次 GC 时才能回收被引用对象
一个对象是否应该在垃圾回收器在GC时回收,至少要经历两次标记过程。
-
第一次标记过程,通过可达性分析算法分析对象是否与
GC Roots可达。经过第一次标记,并且被筛选为不可达的对象会进行第二次标记。 -
第二次标记过程,判断不可达对象是否有必要执行
finalize方法。执行条件是当前对象的finalize方法被重写,并且还未被系统调用过。如果允许执行那么这个对象将会被放到一个叫F-Query的队列中,等待被执行。
注意:由于finalize由一个优先级比较低的Finalizer线程运行,所以该对象的的finalize方法不一定被执行,即使被执行了,也不保证finalize方法一定会执行完。如果对象第二次小规模标记,即finalize方法中拯救自己,只需要重新和引用链上的任一对象建立关联即可。
代码案例如下 :
package cn.knightzz.reference.final_ref; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: FinalReferenceTest * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 终结器引用 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-12 21:52 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class FinalReferenceTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc My my = new My(); System.out.println("请回车 : "); System.in.read(); my = null; System.gc(); System.out.println("请回车 : "); System.in.read(); } } class My { @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " do finalize..."); } }
运行结果如下 :
请回车 : [GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 3116K->488K(6144K)] 3116K->1165K(19968K), 0.0007622 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (System.gc()) [PSYoungGen: 488K->0K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 677K->1100K(13824K)] 1165K->1100K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3740K->3740K(1056768K)], 0.0083840 secs] [Times: user=0.09 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs] 请回车 : Thread[Finalizer,8,system] do finalize... Heap PSYoungGen total 6144K, used 150K [0x00000000ff980000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) eden space 5632K, 2% used [0x00000000ff980000,0x00000000ff9a5aa0,0x00000000fff00000) from space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff80000) to space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff80000,0x00000000fff80000,0x0000000100000000) ParOldGen total 13824K, used 1100K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff980000, 0x00000000ff980000) object space 13824K, 7% used [0x00000000fec00000,0x00000000fed131d0,0x00000000ff980000) Metaspace used 3746K, capacity 4540K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 410K, capacity 428K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到上面的运行结果 : 当我们点击回车后, 执行垃圾回收, 此时 因为 my = null, My对象已经没有了引用, 所以垃圾回收的时候会直接回收掉, 回收的时候会执行
类的 finalize 方法
引用总结
Java中4种引用的级别和强度由高到低依次为:强引用 -> 软引用 -> 弱引用 -> 虚引用
当垃圾回收器回收时,某些对象会被回收,某些不会被回收。垃圾回收器会从根对象Object来标记存活的对象,然后将某些不可达的对象和一些引用的对象进行回收。
通过表格来说明一下,如下:
| 引用类型 | 被垃圾回收时间 | 用途 | 生存时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 强引用 | 从来不会 | 对象的一般状态 | JVM停止运行时终止 |
| 软引用 | 当内存不足时 | 对象缓存 | 内存不足时终止 |
| 弱引用 | 正常垃圾回收时 | 对象缓存 | 垃圾回收后终止 |
| 虚引用 | 正常垃圾回收时 | 跟踪对象的垃圾回收 | 垃圾回收后终止 |
番外-引用队列
引用队列可以与软引用、弱引用以及虚引用一起配合使用,当垃圾回收器准备回收一个对象时,如果发现它还有引用,那么就会在回收对象之前,把这个引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中去。程序可以通过判断引用队列中是否已经加入了引用,来判断被引用的对象是否将要被垃圾回收,这样就可以在对象被回收之前采取一些必要的措施。
与软引用、弱引用不同,虚引用必须和引用队列一起使用。
ReferenceQueue内部数据结构是一个链表,链表里的元素是加入进去的Reference实例,然后通过wait和notifyAll与对象锁实现生产者和消费者,通过这种方式模拟一个队列。
ReferenceQueue是使用wati()和notifyAll()实现生产者和消费者模式的一个具体场景。
ReferenceQueue重点源码解析:
static ReferenceQueue<Object> NULL = new Null<>(); static ReferenceQueue<Object> ENQUEUED = new Null<>();
这两个静态属性主要用于标识加入引用队列的引用的状态,NULL标识该引用已被当前队列移除过,ENQUEUED标识该引用已加入当前队列。
boolean enqueue(Reference<? extends T> r) { /* Called only by Reference class */ synchronized (lock) { //检查该引用是否曾从当前队列移除过或者已经加入当前队列了,如果有则直接返回 ReferenceQueue<?> queue = r.queue; if ((queue == NULL) || (queue == ENQUEUED)) { return false; } assert queue == this; r.queue = ENQUEUED;//将引用关联的队列统一标识为ENQUEUED r.next = (head == null) ? r : head;//当前引用指向head head = r; //将head指向当前引用(链表新增节点采用头插法) queueLength++; //更新链表长度 if (r instanceof FinalReference) { sun.misc.VM.addFinalRefCount(1); // } lock.notifyAll(); //通知消费端 return true; } }
引用队列入队流程 :
-
加锁
-
检查该引用是否曾从当前队列移除过或者已经加入当前队列了,如果有则直接返回
-
将引用关联的队列统一标识为ENQUEUED : (
ENQUEUED标识该引用已加入当前队列。) -
将当前引用插入队列 (引用队列是由链表实现的)
-
更新引用队列的长度
-
解锁
移除源码如下 :
public Reference<? extends T> remove(long timeout) throws IllegalArgumentException, InterruptedException { if (timeout < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative timeout value"); } synchronized (lock) { Reference<? extends T> r = reallyPoll(); if (r != null) return r; //如果成功移除则直接返回 long start = (timeout == 0) ? 0 : System.nanoTime(); for (;;) { lock.wait(timeout); //释放当前线程锁,等待notify通知唤醒 r = reallyPoll(); if (r != null) return r; if (timeout != 0) { //如果超时时间不为0则校验超时 long end = System.nanoTime(); timeout -= (end - start) / 1000_000; if (timeout <= 0) return null; //如果剩余时间小于0则返回 start = end; } } } }
remove尝试移除队列中的头部元素,如果队列为空则一直等待直至达到指定的超时时间。
案例
GC Roots
MAE(Eclipse Memory Analyzer) 下载地址 : https://www.eclipse.org/mat/downloads.php
package cn.knightzz.gc; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: GcRootsTest * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: GC测试 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-09 19:10 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") @Slf4j(topic = "c.GcRootsTest") public class GcRootsTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException { List<Object> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); list1.add("a"); list1.add("b"); System.out.println(1); System.in.read(); list1 = null; System.out.println(2); System.in.read(); System.out.println("end..."); } }
我们可以使用 jps 命令查看进程ID :
knight'z'z@DESKTOP-VAQG1TR MINGW64 /f/JavaCode/hm-jvm-codes (master) $ jps 43520 GcRootsTest 59520 Jps 8096 org.eclipse.equinox.launcher_1.6.400.v20210924-0641.jar 18372 20532 59352 Launcher 41852 RemoteMavenServer36
然后生成对应的快照 jmap -dump:format=b,live,file=GcRootTest2.bin 43520 快照名字 GcRootTest2.bin
我们可以通过MAE加载快照来查看 GC Roots
软引用案例
仅有软引用引用该对象时,在垃圾回收(GC)后,内存仍不足时会再次出发垃圾回收,回收软引用对象 , 回收以后软引用对象就变成了 null
package cn.knightzz.reference.soft; import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.ref.SoftReference; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: SoftRefferenceTest * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 测试软引用 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-10 11:06 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class SoftReferenceTest { private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 演示软引用 // -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc // strongReference(); soft(); } private static void strongReference() throws IOException { List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("run ==> " + i + "..."); list.add(new byte[_4MB]); } System.in.read(); } public static void soft() { // list --> SoftReference --> byte[] List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { SoftReference<byte[]> ref = new SoftReference<>(new byte[_4MB]); System.out.println("Reference : " + ref.get()); list.add(ref); System.out.println("List Reference Size : " + list.size()); } System.out.println("循环结束:" + list.size()); for (SoftReference<byte[]> ref : list) { System.out.println(ref.get()); } } }
我们首先要执行强引用的演示代码 strongReference() , 执行时需要加上JVM参数 : -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc
run ==> 1... run ==> 2... run ==> 3... run ==> 4... [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 2176K->488K(6144K)] 14464K->13093K(19968K), 0.0006766 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] run ==> 5... [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4696K->4696K(6144K)] 17302K->17390K(19968K), 0.0004525 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Ergonomics) [PSYoungGen: 4696K->4510K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12693K->12641K(13824K)] 17390K->17151K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3238K->3238K(1056768K)], 0.0039242 secs] [Times: user=0.11 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4510K->4510K(6144K)] 17151K->17183K(19968K), 0.0004882 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4510K->4491K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12673K->12642K(13824K)] 17183K->17134K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3238K->3238K(1056768K)], 0.0042548 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] Heap PSYoungGen total 6144K, used 4660K [0x00000000ff980000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) eden space 5632K, 82% used [0x00000000ff980000,0x00000000ffe0d220,0x00000000fff00000) from space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff80000) to space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff80000,0x00000000fff80000,0x0000000100000000) ParOldGen total 13824K, used 12642K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff980000, 0x00000000ff980000) object space 13824K, 91% used [0x00000000fec00000,0x00000000ff8589c8,0x00000000ff980000) Metaspace used 3269K, capacity 4500K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 354K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at cn.knightzz.reference.soft.SoftReferenceTest.strongReference(SoftReferenceTest.java:35) at cn.knightzz.reference.soft.SoftReferenceTest.main(SoftReferenceTest.java:26)
可以看到上面的运行结果, 前四次都可以正常执行, 但是执行完JVM内存不足, 执行了一次 Mini GC : GC (Allocation Failure) , 但是回收以后内存还是不足, 所以又再次执行了 Full GC :
[GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4696K->4696K(6144K)] 17302K->17390K(19968K), 0.0004525 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Ergonomics) [PSYoungGen: 4696K->4510K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12693K->12641K(13824K)] 17390K->17151K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3238K->3238K(1056768K)], 0.0039242 secs] [Times: user=0.11 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4510K->4510K(6144K)] 17151K->17183K(19968K), 0.0004882 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4510K->4491K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12673K->12642K(13824K)] 17183K->17134K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3238K->3238K(1056768K)], 0.0042548 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]
但是因为是强引用, 即使多次执行了GC也无法清理出足够的内存, 所以JVM出现了内存溢出 :
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at cn.knightzz.reference.soft.SoftReferenceTest.strongReference(SoftReferenceTest.java:35) at cn.knightzz.reference.soft.SoftReferenceTest.main(SoftReferenceTest.java:26)
然后我们在Byte数组外包裹一层 SoftReference , 执行 soft() 方法
Reference : [B@66d3c617 List Reference Size : 1 Reference : [B@63947c6b List Reference Size : 2 Reference : [B@2b193f2d List Reference Size : 3 [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 2176K->488K(6144K)] 14464K->13089K(19968K), 0.0005755 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] Reference : [B@355da254 List Reference Size : 4 [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4696K->4696K(6144K)] 17298K->17362K(19968K), 0.0004850 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Ergonomics) [PSYoungGen: 4696K->4522K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12665K->12629K(13824K)] 17362K->17152K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3238K->3238K(1056768K)], 0.0039546 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4522K->4522K(6144K)] 17152K->17184K(19968K), 0.0003913 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4522K->0K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12661K->750K(8704K)] 17184K->750K(14848K), [Metaspace: 3238K->3238K(1056768K)], 0.0055147 secs] [Times: user=0.16 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs] Reference : [B@4dc63996 List Reference Size : 5 循环结束:5 null null null null [B@4dc63996 Heap PSYoungGen total 6144K, used 4264K [0x00000000ff980000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) eden space 5632K, 75% used [0x00000000ff980000,0x00000000ffdaa370,0x00000000fff00000) from space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff80000) to space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff80000,0x00000000fff80000,0x0000000100000000) ParOldGen total 8704K, used 750K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff480000, 0x00000000ff980000) object space 8704K, 8% used [0x00000000fec00000,0x00000000fecbba50,0x00000000ff480000) Metaspace used 3245K, capacity 4500K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 351K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
执行结果如上, 可以看到执行到第3次的时候出现了内存不足的情况, 这个时候JVM执行了一次 mini GC , 然后再执行到第四次后内存还是不够, 开始执行 Full GC
但是需要注意啊 : 软引用 在垃圾回收(GC)后,内存仍不足时会再次出发垃圾回收,回收软引用对象 , 回收以后软引用对象就变成了 null
可以看到在循环结束以后, 前四个对象都被回收了, 变成了null
软引用-引用队列
我们可以创建引用队列 ReferenceQueue<byte[]> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>(); , 让被移除的对象加入到引用队列中
运行时需要添加JVM参数 : -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc
package cn.knightzz.reference.soft; import java.lang.ref.Reference; import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue; import java.lang.ref.SoftReference; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: SoftReferenceQueueTest * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 软引用队列 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-10 17:04 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class SoftReferenceQueueTest { private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024; public static void main(String[] args) { List<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 引用队列 ReferenceQueue<byte[]> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // 关联了引用队列, 当软引用所关联的 byte[]被回收时,软引用自己会加入到 queue 中去 SoftReference<byte[]> ref = new SoftReference<>(new byte[_4MB], queue); System.out.println(ref.get()); list.add(ref); System.out.println(list.size()); } // 从队列中获取无用的 软引用对象,并移除 // 遍历队列, 返回可用的软引用对象, 如果软引用对象已经被垃圾回收了, 就返回null Reference<? extends byte[]> poll = queue.poll(); // size = 4 while (poll != null) { list.remove(poll); poll = queue.poll(); } System.out.println("==========================="); for (SoftReference<byte[]> reference : list) { System.out.println(reference.get()); } } }
我们在创建软引用的时候就在构造参数里面传入 queue 来和软引用对象进行关联, 当软引用所关联的 byte[]被回收时,软引用自己会加入到 queue 中去, 代码运行结果如下 :
[B@66d3c617 1 [B@63947c6b 2 [B@2b193f2d 3 [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 2176K->512K(6144K)] 14464K->13081K(19968K), 0.0014408 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@355da254 4 [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4720K->4720K(6144K)] 17289K->17353K(19968K), 0.0009495 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Ergonomics) [PSYoungGen: 4720K->4560K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12633K->12590K(13824K)] 17353K->17151K(19968K), [Metaspace: 3236K->3236K(1056768K)], 0.0038709 secs] [Times: user=0.02 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [GC (Allocation Failure) --[PSYoungGen: 4560K->4560K(6144K)] 17151K->17215K(19968K), 0.0005702 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4560K->0K(6144K)] [ParOldGen: 12654K->750K(8704K)] 17215K->750K(14848K), [Metaspace: 3236K->3236K(1056768K)], 0.0048210 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs] [B@4dc63996 5 =========================== [B@4dc63996 Heap PSYoungGen total 6144K, used 4264K [0x00000000ff980000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) eden space 5632K, 75% used [0x00000000ff980000,0x00000000ffdaa348,0x00000000fff00000) from space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff80000) to space 512K, 0% used [0x00000000fff80000,0x00000000fff80000,0x0000000100000000) ParOldGen total 8704K, used 750K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff480000, 0x00000000ff980000) object space 8704K, 8% used [0x00000000fec00000,0x00000000fecbb8d8,0x00000000ff480000) Metaspace used 3243K, capacity 4500K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 350K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
可以看到, 第三次执行完成以后 JVM执行了一次 mini GC, 然后执行第四次循环, 但是内存依然不够, 然后就又执行了多次 Mini GC 和 Full GC , 软引用在执行第二次GC的时候会被回收掉
所以看到下面仅仅只有最后一个软引用对象 [B@4dc63996 被保留.
弱引用
弱引用的使用方式和软引用一样, 使用 WeakReference 对象包裹需要引用的类型即可
package cn.knightzz.reference.weak; import java.lang.ref.WeakReference; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: WeakReferenceTest * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 弱引用测试 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-10 17:05 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class WeakReferenceTest { private static final int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024; public static void main(String[] args) { // -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc weakReference(); } public static void weakReference() { // list --> WeakReference --> byte[] List<WeakReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { WeakReference<byte[]> ref = new WeakReference<>(new byte[_4MB]); list.add(ref); for (WeakReference<byte[]> w : list) { System.out.print(w.get() + " "); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("循环结束:" + list.size()); } }
软引用是在经过第二次GC的时候就会被回收, 而弱引用是触发GC的时候顶部的引用对象就会被回收掉, 即使当前内存并没有溢出 , 触发GC一般是新增引用对象的时候, 内存不足才会触发GC
执行结果如下 :
[B@66d3c617 [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 2176K->504K(6144K)] 14464K->13084K(19968K), 0.0006344 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d [B@355da254 [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4712K->480K(6144K)] 17293K->13188K(19968K), 0.0004976 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d null [B@4dc63996 [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4688K->504K(6144K)] 17396K->13252K(19968K), 0.0002994 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d null null [B@d716361 [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4711K->488K(6144K)] 17459K->13252K(19968K), 0.0002793 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d null null null [B@6ff3c5b5 [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4694K->496K(6144K)] 17459K->13300K(19968K), 0.0003121 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d null null null null [B@3764951d [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4702K->504K(5120K)] 17506K->13308K(18944K), 0.0002751 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d null null null null null [B@4b1210ee [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4690K->32K(5632K)] 17494K->13256K(19456K), 0.0003160 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Ergonomics) [PSYoungGen: 32K->0K(5632K)] [ParOldGen: 13224K->768K(8192K)] 13256K->768K(13824K), [Metaspace: 3237K->3237K(1056768K)], 0.0048700 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] null null null null null null null null null [B@4d7e1886 循环结束:10 Heap PSYoungGen total 5632K, used 4278K [0x00000000ff980000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) eden space 4608K, 92% used [0x00000000ff980000,0x00000000ffdadb30,0x00000000ffe00000) from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ffe00000,0x00000000ffe00000,0x00000000fff00000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000fff00000,0x00000000fff00000,0x0000000100000000) ParOldGen total 8192K, used 768K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff980000) object space 8192K, 9% used [0x00000000fec00000,0x00000000fecc00b8,0x00000000ff400000) Metaspace used 3245K, capacity 4500K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 350K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
可以看到上面的结果 :
[GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4712K->480K(6144K)] 17293K->13188K(19968K), 0.0004976 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [B@66d3c617 [B@63947c6b [B@2b193f2d null [B@4dc63996
在添加第五个元素的时候因为内存不足触发了GC , 可以看到触发了GC以后直接就回收了最近添加的弱引用对象, 后面以此类推, 只要触发了GC, 就直接回收弱引用对象,
可以看到在最后面, 新添加 [B@4d7e1886 引用对象内存不足的时候直接执行了 Full GC, 把所有的弱引用对象直接清除了.
垃圾回收算法
标记清除
算法介绍
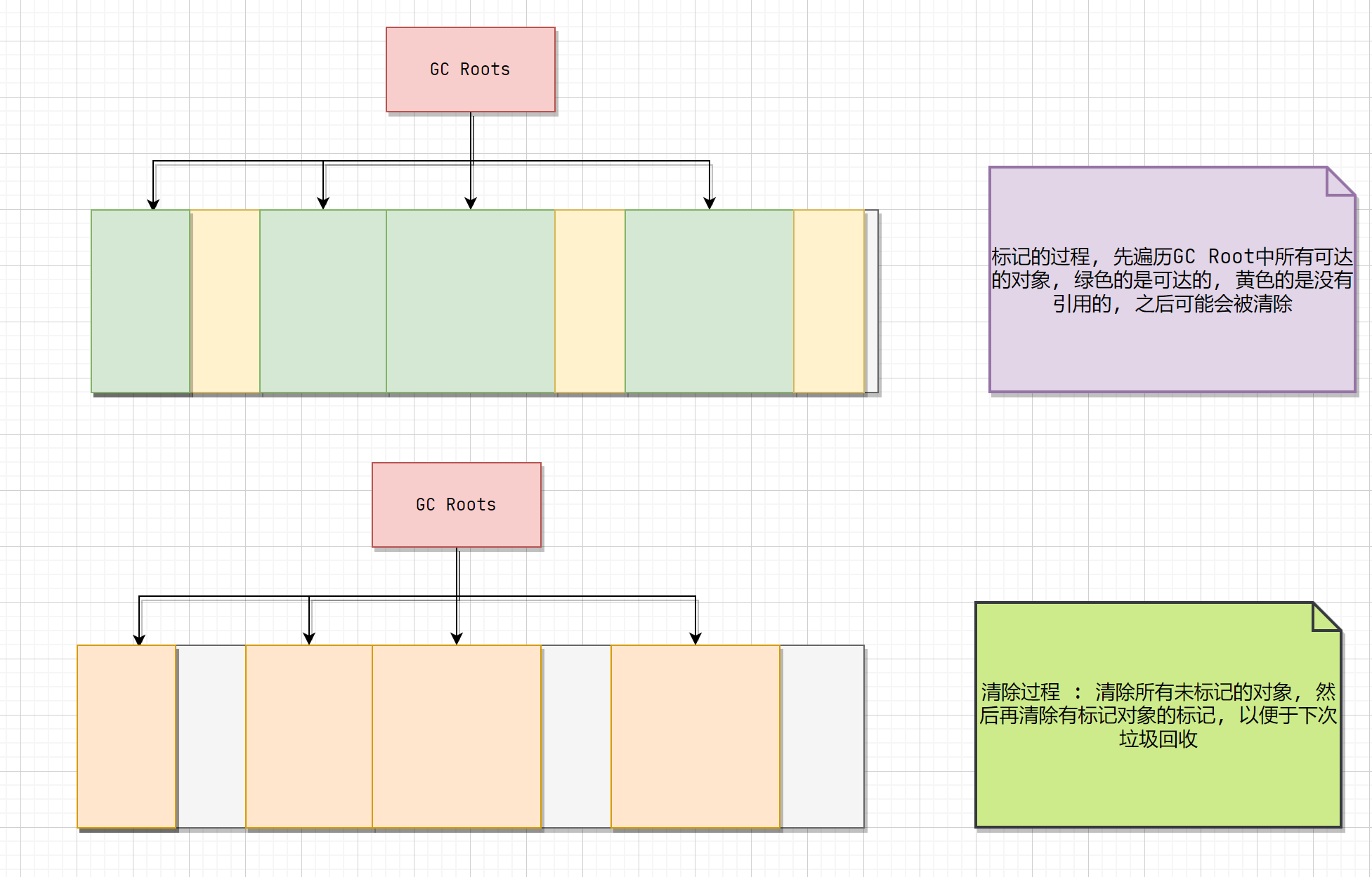
标记的过程是:遍历所有的 GC Roots,然后将所有 GC Roots 可达的对象标记为存活的对象
清除的过程将遍历堆中所有的对象,将没有标记的对象全部清除掉。与此同时,清除那些被标记过的对象的标记,以便下次的垃圾回收。
存在的问题 :
- 效率问题:标记和清除两个过程的效率都不高。
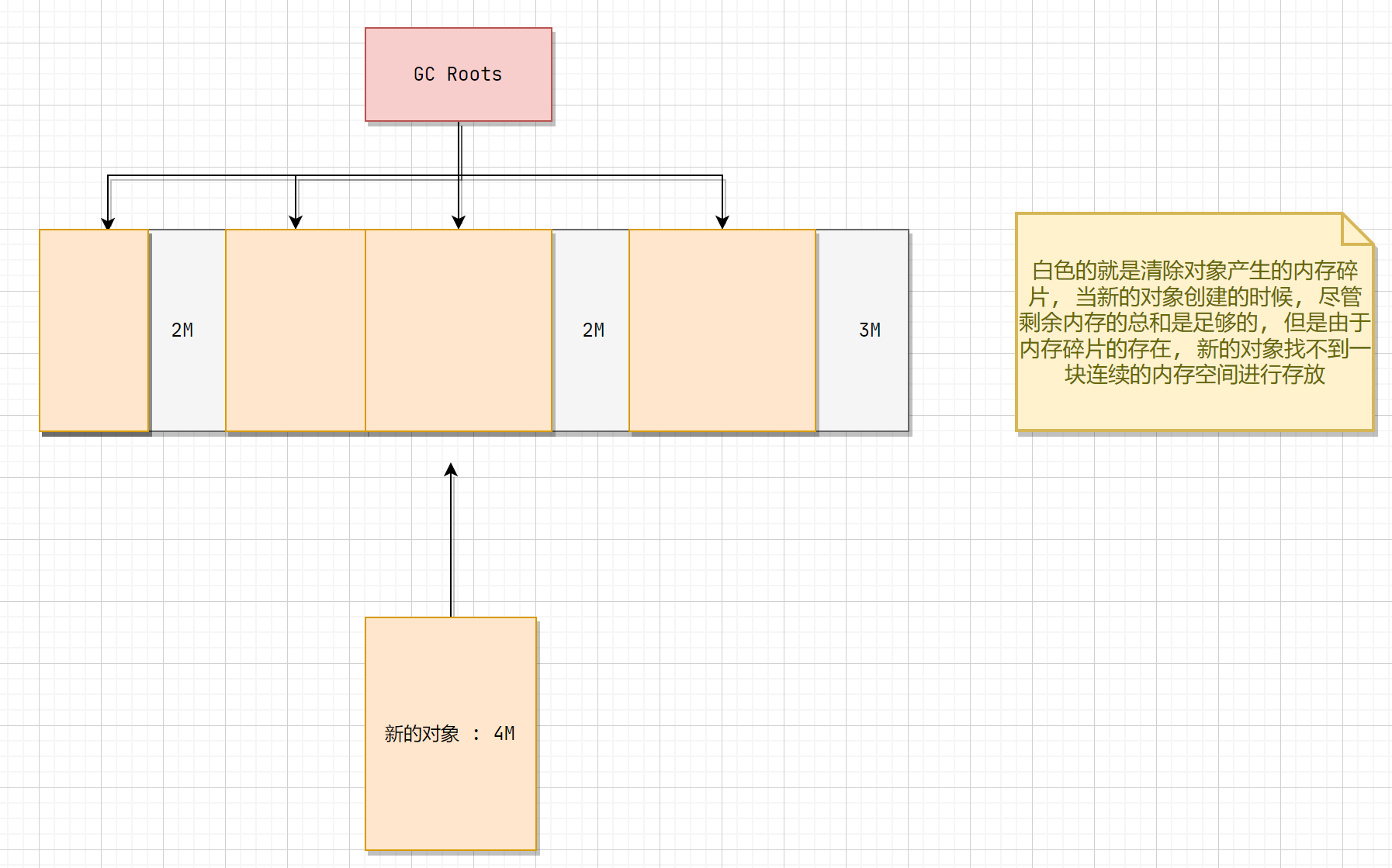
- 空间问题:标记清除之后会产生大量不连续的内存碎片,碎片太多可能导致以后需要分配较大对象时,无法找到足够的连续内存而不得不提前触发另一次垃圾收集动作
标记清除图解
标记清除的过程
存在的内存碎片问题 :
标记整理
基本介绍
标记-整理算法 采用和 标记-清除算法 一样的方式进行对象的标记,但后续不直接对可回收对象进行清理,而是将所有的存活对象往一端空闲空间移动,然后清理掉端边界以外的内存空间。
-
优点:
解决了标记-清理算法存在的内存碎片问题。
-
缺点:
仍需要进行局部对象移动,一定程度上降低了效率, 因为对象的移动涉及到拷贝以及内存地址的改变
标记整理图解

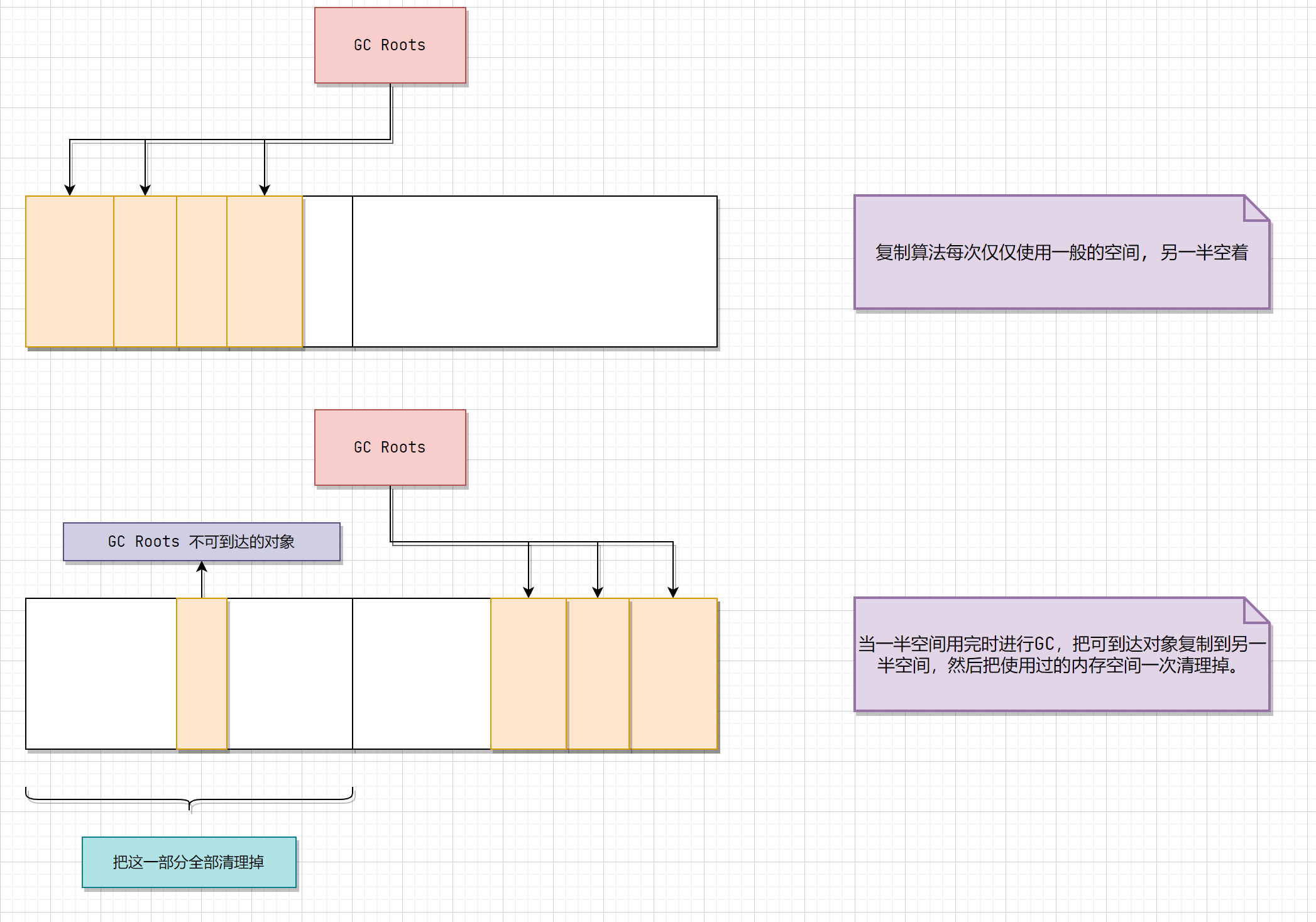
复制算法
基本介绍
这种收集算法解决了标记清除算法存在的效率问题。它将内存区域划分成相同的两个内存块。每次仅使用一半的空间,JVM生成的新对象放在一半空间中。当一半空间用完时进行GC,把可到达对象复制到另一半空间,然后把使用过的内存空间一次清理掉。
-
优点:
按顺序分配内存即可,实现简单、运行高效,不用考虑内存碎片。
-
缺点:
可用的内存大小缩小为原来的一半,对象存活率高时会频繁进行复制。
复制算法详解
分代回收
基本介绍
对象首先分配在伊甸园区域(endn)
新生代空间不足时,触发 minor gc,伊甸园和 from 存活的对象使用 copy 复制到 to 中,存活的对象年龄加 1并且交换 from to,
minor gc 会引发 stop the world,暂停其它用户的线程,等垃圾回收结束,用户线程才恢复运行
当对象寿命超过阈值时,会晋升至老年代,最大寿命是15(4bit)
当老年代空间不足,会先尝试触发 minor gc,如果之后空间仍不足,那么触发 full gc,STW 的时间更长
当前商业虚拟机都采用分代收集的垃圾收集算法。分代收集算法,顾名思义是根据对象的存活周期将内存划分为几块。一般包括年轻代、老年代 和 永久代,如图所示:
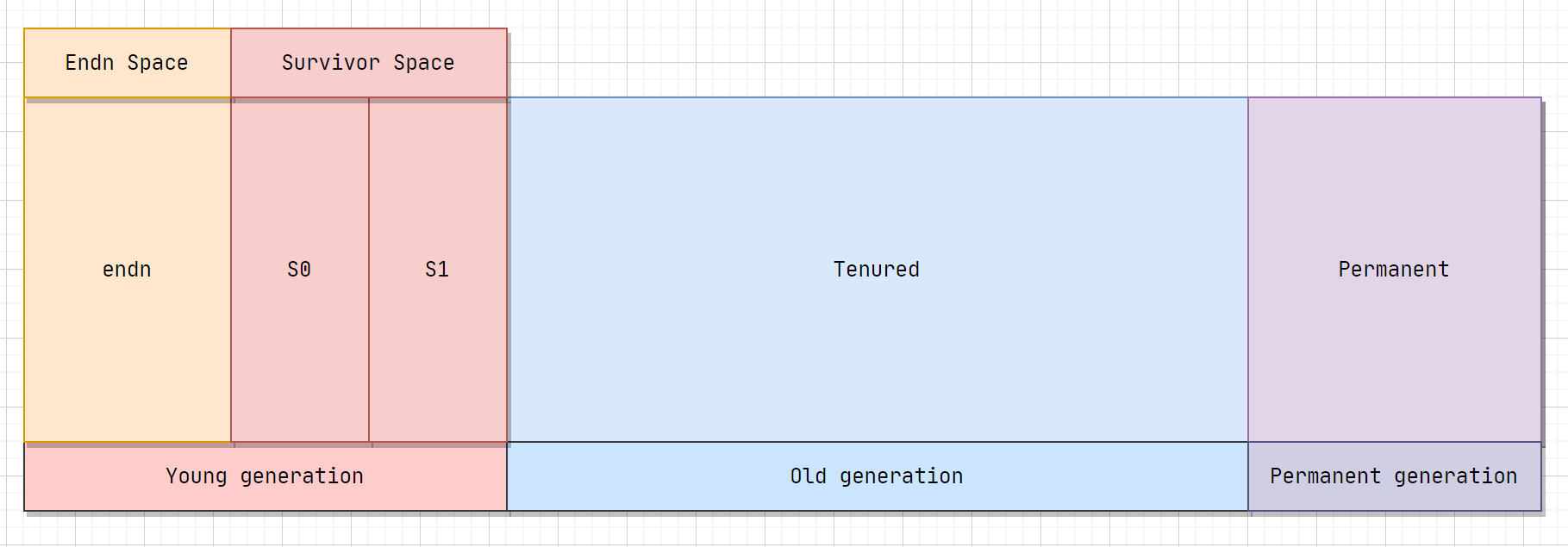
新生代(Young generation)
绝大多数最新被创建的对象会被分配到这里,由于大部分对象在创建后会很快变得不可达,所以很多对象被创建在新生代,然后消失。对象从这个区域消失的过程我们称之为 minor GC。
新生代 中存在一个Eden区和两个Survivor区 :
- 新对象会首先分配在
Eden中(如果新对象过大,会直接分配在老年代中)。 - 在
GC中,Eden中的对象会被移动到Survivor中,直至对象满足一定的年纪(定义为熬过GC的次数),会被移动到老年代。
可以设置新生代和老年代的相对大小。这种方式的优点是新生代大小会随着整个堆大小动态扩展。参数 -XX:NewRatio 设置老年代与新生代的比例。例如 -XX:NewRatio=8 指定 老年代/新生代 为8/1. 老年代 占堆大小的 7/8 ,新生代 占堆大小的 1/8(默认即是 1/8)。
-XX:NewSize=64m -XX:MaxNewSize=1024m -XX:NewRatio=8
老年代(Old generation)
对象没有变得不可达,并且从新生代中存活下来,会被拷贝到这里。其所占用的空间要比新生代多。也正由于其相对较大的空间,发生在老年代上的GC要比新生代要少得多。对象从老年代中消失的过程,可以称之为major GC(或者full GC)
永久代(permanent generation)
像一些类的层级信息,方法数据 和方法信息(如字节码,栈 和 变量大小),运行时常量池(JDK7之后移出永久代),已确定的符号引用和虚方法表等等。它们几乎都是静态的并且很少被卸载和回收,在JDK8之前的HotSpot虚拟机中,类的这些永久的 数据存放在一个叫做永久代的区域。
永久代一段连续的内存空间,我们在JVM启动之前可以通过设置-XX:MaxPermSize的值来控制永久代的大小。但是JDK8之后取消了永久代,这些元数据被移到了一个与堆不相连的称为元空间 (Metaspace) 的本地内存区域。
总结
JDK8堆内存一般是划分为年轻代和老年代,不同年代 根据自身特性采用不同的垃圾收集算法。
-
对于新生代,每次
GC时都有大量的对象死亡,只有少量对象存活。考虑到复制成本低,适合采用复制算法。因此有了From Survivor和To Survivor区域。 -
对于老年代,因为对象存活率高,没有额外的内存空间对它进行担保。因而适合采用标记-清理算法和标记-整理算法进行回收。
GC相关
JVM相关参数
| 参数名称 | 参数配置 |
|---|---|
| 堆初始大小 | -Xms |
| 堆最大大小 | -Xmx 或 -XX |
| 新生代大小 | -Xmn 或 (-XX |
| 幸存区比例(动态) | -XX |
| 幸存区比例 | -XX |
| 晋升阈值 | -XX |
| 晋升详情 | -XX:+PrintTenuringDistribution |
| GC详情 | -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose |
| FullGC 前 MinorGC | -XX:+ScavengeBeforeFullGC |
GC分析
默认情况
默认参数 : -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc -XX:-ScavengeBeforeFullGC
- 推初始大小 20M
- 新生代大小 10M (实际是9M, Survivor Space 使用的是复制算法, 仅能使用一般的空间)
- GC详情 -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose
- FullGC 前 MinorGC -XX:+ScavengeBeforeFullGC
package cn.knightzz.gc.analysis; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: GcAnalysisTest01 * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 演示内存的分配策略 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-13 16:26 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class GcAnalysisTest01 { private static final int _512KB = 512 * 1024; private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024; private static final int _6MB = 6 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _7MB = 7 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _8MB = 8 * 1024 * 1024; // -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc -XX:-ScavengeBeforeFullGC public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { } }
在不执行任何代码的情况下, 执行结果如下 :
Heap def new generation total 9216K, used 2379K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) eden space 8192K, 29% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000fee52f60, 0x00000000ff400000) from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff600000) tenured generation total 10240K, used 0K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) the space 10240K, 0% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600200, 0x0000000100000000) Metaspace used 3156K, capacity 4496K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 343K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到默认的情况下: new generation total 9216K , to 占用1M , 在GC中,Eden中的对象会被移动到Survivor中,直至对象满足一定的年纪(定义为熬过GC的次数),会被移动到老年代。
新生代
由上面的代码我们可以知道, eden 可用的空间有 8192k 左右, 最大可用内存在7M左右(实际要更小一些), 下面的代码测试 :
package cn.knightzz.gc.analysis; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: GcAnalysisTest01 * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 演示内存的分配策略 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-13 16:26 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class GcAnalysisTest01 { private static final int _512KB = 512 * 1024; private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024; private static final int _6MB = 6 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _7MB = 7 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _8MB = 8 * 1024 * 1024; // -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc -XX:-ScavengeBeforeFullGC public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ArrayList<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new byte[_7MB]); list.add(new byte[_512KB]); } }
执行结果如下所示 :
[GC (Allocation Failure) [DefNew: 2051K->759K(9216K), 0.0022163 secs] 2051K->759K(19456K), 0.0022642 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.02, real=0.00 secs] Heap def new generation total 9216K, used 8951K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) eden space 8192K, 100% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000) from space 1024K, 74% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff5bdcb8, 0x00000000ff600000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) tenured generation total 10240K, used 0K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) the space 10240K, 0% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600200, 0x0000000100000000) Metaspace used 3226K, capacity 4496K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 348K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到, eden区域放不下, 所以一部分放到了 survivor 区域
老年代
两种情况下对象会由新生代转移到老年代 :
- 内存对象过大, 新生代存储空间不够, 所以就直接放到了老年代
- 经历多次 GC , 对象没有变得不可达,并且从新生代中存活下来,会被拷贝到这里
新生代存储空间不足的情况 :
package cn.knightzz.gc.analysis; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: GcAnalysisTest01 * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 演示内存的分配策略 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-13 16:26 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class GcAnalysisTest01 { private static final int _512KB = 512 * 1024; private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024; private static final int _6MB = 6 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _7MB = 7 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _8MB = 8 * 1024 * 1024; // -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc -XX:-ScavengeBeforeFullGC public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ArrayList<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new byte[_8MB]); } }
执行结果如下 :
Heap def new generation total 9216K, used 2379K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) eden space 8192K, 29% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000fee52f60, 0x00000000ff400000) from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff600000) tenured generation total 10240K, used 8192K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) the space 10240K, 80% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ffe00010, 0x00000000ffe00200, 0x0000000100000000) Metaspace used 3234K, capacity 4496K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 349K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到 Byte数组对象的大小是8M, 比较大, 新生代是存不下的, 所以直接存入了老年代里面, 可以看到占用率是 80%, 老年代大小是 10M, 80%正好是 8M
经过多次GC的情况:
package cn.knightzz.gc.analysis; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: GcAnalysisTest01 * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 演示内存的分配策略 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-13 16:26 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class GcAnalysisTest01 { private static final int _512KB = 512 * 1024; private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024; private static final int _6MB = 6 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _7MB = 7 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _8MB = 8 * 1024 * 1024; // -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc -XX:-ScavengeBeforeFullGC public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ArrayList<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new byte[_1MB]); System.gc(); System.gc(); } }
执行结果如下 :
[Full GC (System.gc()) [Tenured: 0K->1762K(10240K), 0.0037343 secs] 3075K->1762K(19456K), [Metaspace: 3144K->3144K(1056768K)], 0.0037959 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (System.gc()) [Tenured: 1762K->1762K(10240K), 0.0015325 secs] 1925K->1762K(19456K), [Metaspace: 3144K->3144K(1056768K)], 0.0015577 secs] [Times: user=0.02 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (System.gc()) [Tenured: 1762K->1770K(10240K), 0.0012607 secs] 1933K->1770K(19456K), [Metaspace: 3144K->3144K(1056768K)], 0.0012808 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] Heap def new generation total 9216K, used 328K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) eden space 8192K, 4% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000fec52040, 0x00000000ff400000) from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff600000) tenured generation total 10240K, used 1770K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) the space 10240K, 17% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff7ba848, 0x00000000ff7baa00, 0x0000000100000000) Metaspace used 3154K, capacity 4496K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 343K, capacity 388K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
即使引用还在, 并且新生代内存充足, 但是对象还是被转移到了老年代中
异常情况
当出现内存溢出的时候, 主线程的方法是否会继续执行 :
package cn.knightzz.gc.analysis; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * @author 王天赐 * @title: GcAnalysisTest01 * @projectName hm-jvm-codes * @description: 演示内存的分配策略 * @website <a href="http://knightzz.cn/">http://knightzz.cn/</a> * @github <a href="https://github.com/knightzz1998">https://github.com/knightzz1998</a> * @create: 2022-09-13 16:26 */ @SuppressWarnings("all") public class GcAnalysisTest01 { private static final int _512KB = 512 * 1024; private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024; private static final int _6MB = 6 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _7MB = 7 * 1024 * 1024; private static final int _8MB = 8 * 1024 * 1024; // -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:+UseSerialGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc -XX:-ScavengeBeforeFullGC public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { ArrayList<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new byte[_8MB]); list.add(new byte[_8MB]); }).start(); System.out.println("sleep start ...."); Thread.sleep(1000L); System.out.println("sleep end ...."); } }
执行结果如下, 可以看到即使
sleep.... [GC (Allocation Failure) [DefNew: 4279K->971K(9216K), 0.0018782 secs][Tenured: 8192K->9161K(10240K), 0.0026880 secs] 12471K->9161K(19456K), [Metaspace: 4125K->4125K(1056768K)], 0.0053229 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [Full GC (Allocation Failure) [Tenured: 9161K->9106K(10240K), 0.0021221 secs] 9161K->9106K(19456K), [Metaspace: 4125K->4125K(1056768K)], 0.0021567 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] Exception in thread "Thread-0" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at cn.knightzz.gc.analysis.GcAnalysisTest01.lambda$main$0(GcAnalysisTest01.java:29) at cn.knightzz.gc.analysis.GcAnalysisTest01$$Lambda$1/2065951873.run(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) Heap def new generation total 9216K, used 1315K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) eden space 8192K, 16% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000fed48cd8, 0x00000000ff400000) from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff600000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) tenured generation total 10240K, used 9106K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) the space 10240K, 88% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ffee4870, 0x00000000ffee4a00, 0x0000000100000000) Metaspace used 4645K, capacity 4734K, committed 4992K, reserved 1056768K class space used 516K, capacity 559K, committed 640K, reserved 1048576K Process finished with exit code 0
垃圾回收器
参考文章
垃圾回收器基本步骤
参考 : 7种jvm垃圾回收器,这次全部搞懂 [推荐]
基本介绍
Java虚拟机规范中对垃圾收集器应该如何实现并没有任何规定,因此不同的厂商、版本的虚拟机所提供的垃圾收集器都可能会有很大差别,并且一般都会提供参数供用户根据自己的应用特点和要求组合出各个年代所使用的收集器。
垃圾回收器在回收的时候有不同的策略 :
-
并行和并发
-
吞吐量偶先
-
响应时间优先
-
Minor GC 和 Full GC
-
串行
-
单线程
-
堆内存较小,适合个人电脑
-
-
吞吐量优先
- 让单位时间内,STW 的时间最短 0.2 0.2 = 0.4,垃圾回收时间占比最低,这样就称吞吐量高
-
响应时间优先
- 多线程
- 堆内存较大,多核 cpu
- 尽可能让单次 STW 的时间最短 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 = 0.5
垃圾收集器
串行
-
单线程
-
堆内存较小,适合个人电脑
设置参数 : -XX:+UseSerialGC = Serial + SerialOld
- Serial 工作在新生代, 采用的是 复制算法
- SerialOld 工作在老年代, 采用的是 标记整理法
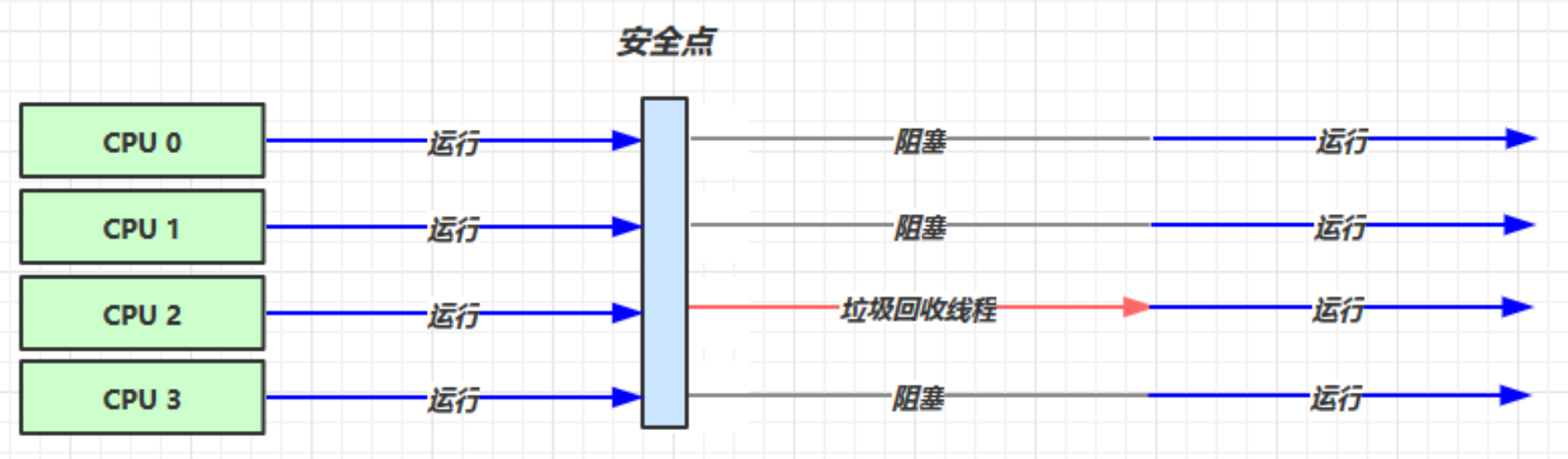
Serial 是单线程的垃圾回收期, 垃圾回程线程运行的时候, 其他线程都要阻塞
并行和并发
并行(Parallel):指多条垃圾收集线程并行工作,但此时用户线程仍然处于等待状态。 并发(Concurrent):指用户线程与垃圾收集线程同时执行(但不一定是并行的,可能会交替执行),用户程序在继续运行。而垃圾收集程序运行在另一个CPU上。
吞吐量优先
吞吐量就是CPU用于运行用户代码的时间与CPU总消耗时间的比值,即吞吐量 = 运行用户代码时间 /(运行用户代码时间 + 垃圾收集时间)。
假设虚拟机总共运行了100分钟,其中垃圾收集花掉1分钟,那吞吐量就是99%
GC 参数 : -XX:+UseParallelGC -XX:+UseParallelOldGC JDK1.8默认开启的
- ParallelGC 默认并行, 应用在新生代
- UseParallelOldGC 标记整理算法, 工作在老年代
GC 参数 : -XX:+UseAdaptiveSizePolicy :
- 采用自适应新生代大小调整策略
GC 参数 : -XX:GCTimeRatio=ratio :
- 调整吞吐量
- 计算公式 : , 假如 radio = 100, result = 0.01 , 只有运行总时间的1%可以用于垃圾回收
- 一般会调整堆的大小, 让堆变大, 提高吞吐量, 但是堆变大, 垃圾回收耗费的时间也会变大
- radio 默认值是 99 , 但是一班设置为 19
GC 参数 : -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=ms :
- 最大暂停毫秒数
- TimeRatio 和 这个参数冲突, 堆空间变小, 垃圾回收时间变小
GC 参数 : -XX:ParallelGCThreads=n :
- 并行垃圾回收的线程数
响应时间优先
- 多线程
- 堆内存较大,多核 cpu
- 尽可能让单次 STW 的时间最短 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 = 0.5
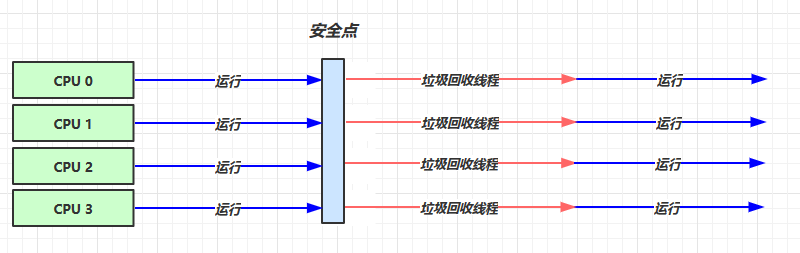
GC 参数 : -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+UseParNewGC
- 开启响应时间优先
- 垃圾回收线程执行的时候, 用户线程也可以并发执行
- 工作在老年代的垃圾回收期
- 如果出现并发问题的话, 就会从 ConcMarkSweepGC 退化成 Serialod 基于标记整理的垃圾回收
GC参数 : -XX:ParallelGCThreads=n , -XX:ConcGCThreads=threads
- 并行与并发的线程数
GC参数 : -XX
-
在垃圾清理的同时会产生新的垃圾(浮动垃圾), 因为是和活动线程并行执行的,
-
但是新的垃圾, 垃圾清理线程不能清理, 因为不能像之前的等到堆内存不足才去清理, 这样新的垃圾就没地方存储了,需要等到下一次垃圾清理的时候进行清理
-
这个参数是控制新的垃圾回收的时机, 即执行垃圾回收的内存占比, 比如 值为 80%, 即老年代内存达到80%时就执行垃圾回收
-
早期的JVM默认值是 65%
GC参数 : -XX:+CMSScavengeBeforeRemark
- 在重新标记之前, 对新生代做一次垃圾回收, 减轻重新标记的压力

- 只有在初始阶段和重新标记节点才会触发 stop-the-world : 执行GC而
停止应用程序的执行
另外 : 如果 CMS 类型的垃圾回收策略并发失败的时候, 会退化成 Serial 策略, 那么相应的相应时间就会变得很长.
本文作者:王天赐
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!